Seq-MRD®
什么是SEQ-MRD®?
Seq-MRD®是一种微小残留病(MRD)的检测方法,适用于某些血液癌症,如白血病、骨髓瘤、淋巴瘤所残留的癌细胞的识别、评估和监控。Seq-MRD®可以用于追踪病患在整个治疗时期不同时间点的MRD水平。
在治疗过程中定期使用Seq-MRD®监测追踪MRD可以在其他检测技术之前发现可能复发的情况。且分子水平的早期复发表现比临床上出现体征和症状的复发表现要更早,医生可更早地对患者及时干预、治疗。
Seq-MRD®分两步检测,如下:
癌细胞“身份”筛查,目的是为了确定待检样本中占主导地位的癌细胞序列,即癌症特异性DNA序列。这对于新加入Seq-MRD®检测的患者是必要的。即临床医生需要提供患者的肿瘤高负荷(初诊或临床复发时)的样本。
癌细胞“追踪”检测,目的是为了评估MRD水平。在完成了上一步克隆性检测之后,再进行一次或多次MRD检测,监测癌细胞克隆是否还存在以及含量多少。Seq-MRD®检测追踪患者在治疗期间或治疗后的血液或骨髓样本中确定的癌症特异性DNA序列。在每次检测过程中,Seq-MRD®还会检测识别出任何新出现的克隆序列。
Seq-MRD®检测原理和技术
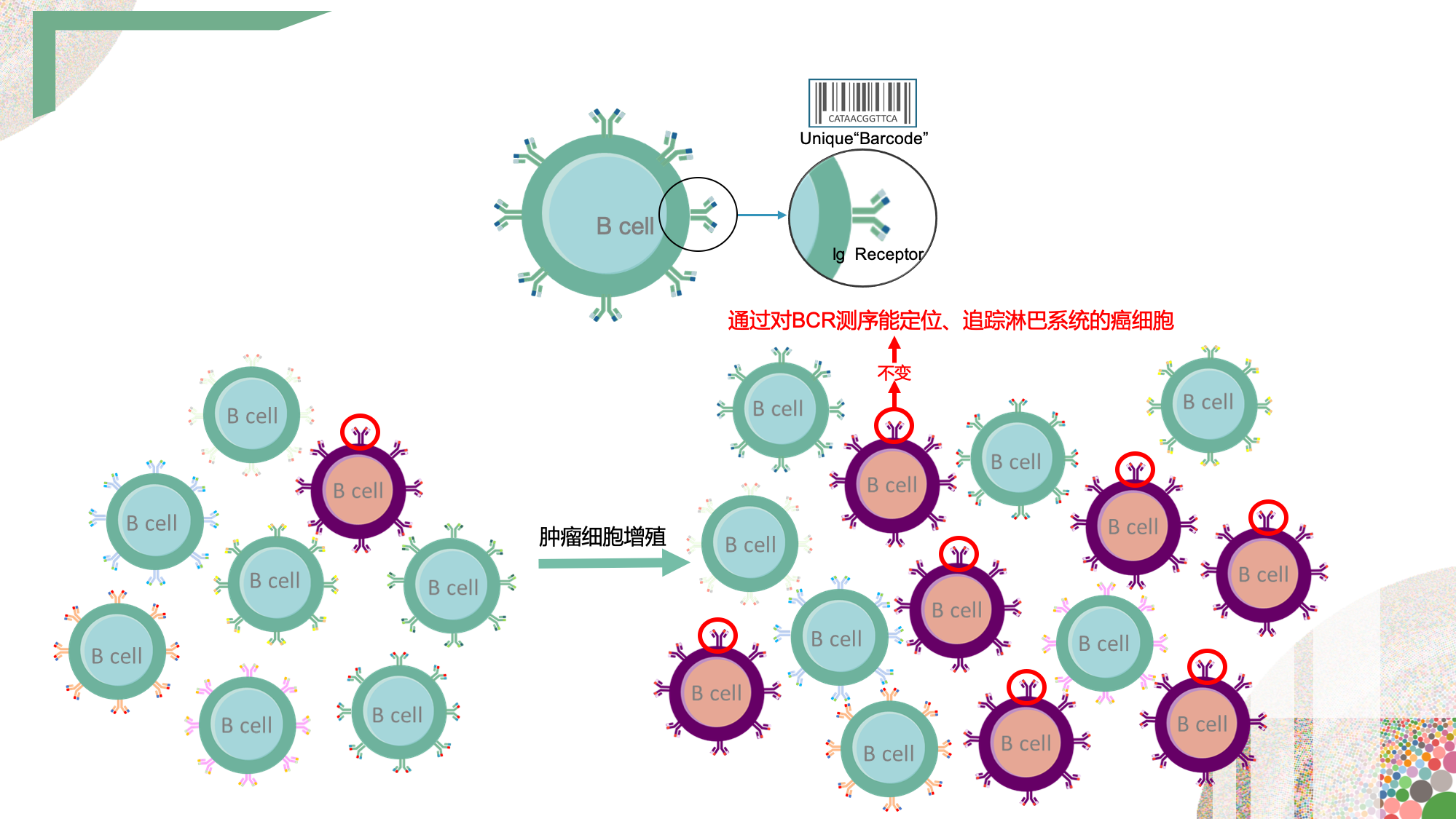
首先在治疗前利用二代测序技术(NGS)筛查出患者癌症特异性的B细胞/T细胞受体(BCR、TCR)序列,再以此追踪检测各治疗阶段和缓解阶段时的状态。但Seq-MRD®不仅仅提供癌细胞是否存在的评估结果。
Seq-MRD®追踪各时期特异性癌细胞序列,同时监测是否有新型癌细胞序列产生,这些可能预示着疾病的进展或复发。高灵敏度地MRD检测能在临床症状出现前预测复发,并评估治疗效果,能让医生更及时地对患者采取干预治疗。
Seq-MRD®技术优势
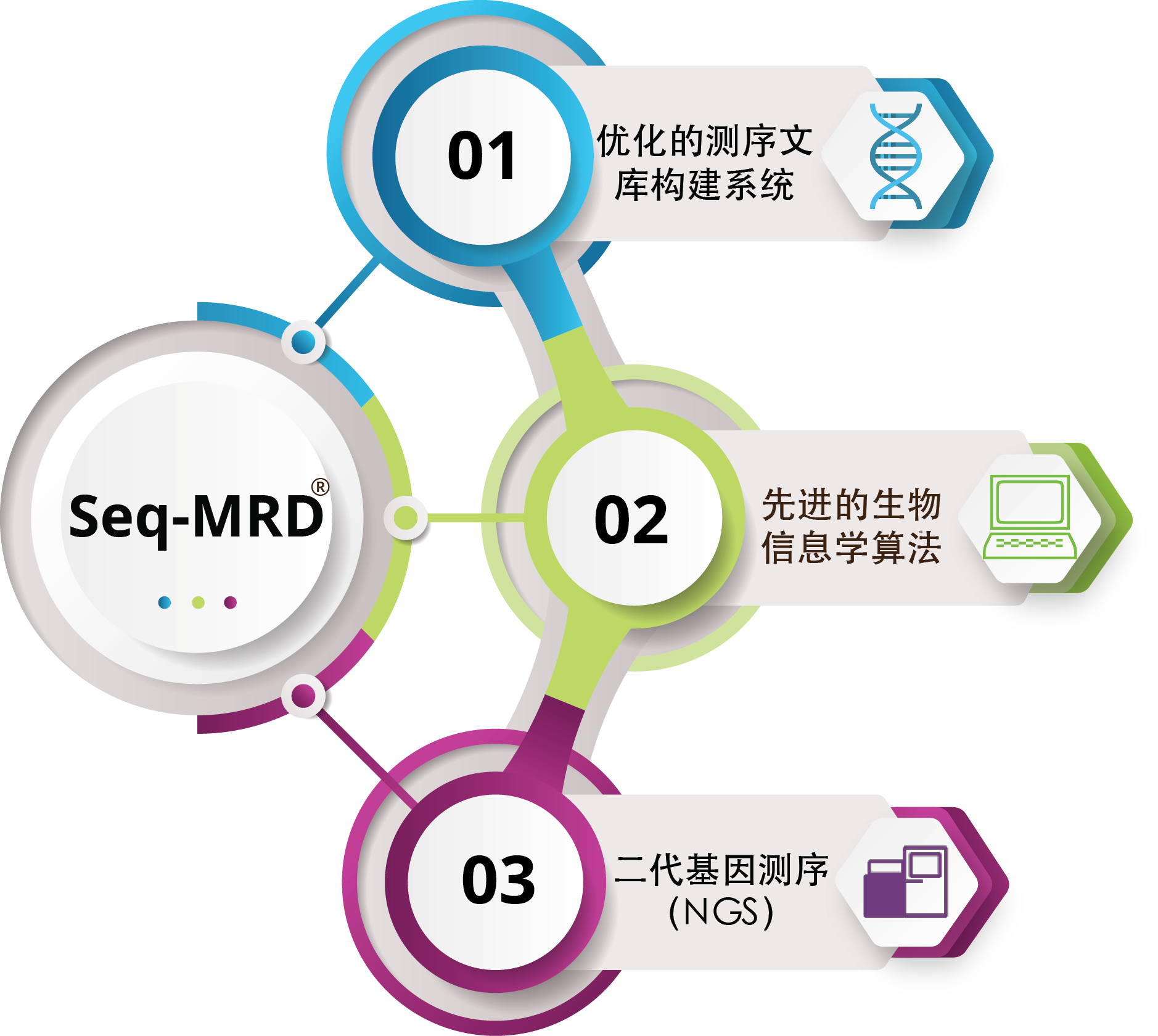
- 【优化文库构建】通过使用合成的能模仿完整的VJ基因分子来调整、优化引物配比,减少多重引物PCR的扩增偏好性,大大提高了NGS测序文库的准确性。
- 【增强定量能力】通过每次检测都会加入的“内参”文库,精确测量“ MRD分母”可最大程度地提高结果的准确性,通过获得样本中包含的总有核细胞数量,来有效地对MRD水平定量。并非使用克隆频率当做MRD值。
- 【提高癌细胞检出率】近百条引物序列包括了对 TRB, TRG, IGH, Incomplete IGH, IGL和IGK这些所有免疫细胞受体链的检测。Seq-MRD可在一次分析中为淋巴细胞恶性肿瘤患者提供免疫受体的全面评估。Seq-MRD不仅可以追踪原有癌细胞序列,还可以检测新出现的癌细胞克隆序列。
- 【(SHM)弹性检测】SHM可导致二代测序方法的MRD的临床检测假阴性或完全检测不到。Seq-MRD提高了对体细胞超突变(SHM)的适应力,最大程度避免SHM对临床MRD结果的影响。
- 【准确判断癌细胞克隆】基于艾沐蒽自建百亿条TCR/BCR数据库筛选出现的“显著性克隆”以获得其独特性指数(Uniqueness Index)来判断是否为癌细胞克隆 。
- 【NGS检测深度】在样本里足够的情况下,NGS 可以在每百万的细胞受体中检测出一个B/T细胞的受体序列。
使用Seq-MRD®作为您MRD监控手段
二代测序方法作为新兴的MRD检测方法,也已受到国内外专家认可并推荐。2017年版国际临床实践指南(NCCN)、2016年版《中国成人急性淋巴细胞白血病诊断与治疗指南》和2017年版《中国多发性骨髓瘤诊治指南》均推荐高通量测序(NGS)作为MRD检测方法。
参考文献:
- Predictive value of next-generation sequencing-based minimal residual disease after CAR-T cell therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant 57, 1350–1353, 2022
-
Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology [NCCN Guidelines®] for Multiple Myeloma V.3.2017. ©National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2017. All rights reserved. Accessed May 11, 2017
-
Deep-sequencing approach for minimal residual disease detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2012;120:5173-5180.
-
Detection of Minimal Residual Disease Using Next Generation Sequencing for Antigen Receptor Gene Rearrangements in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia June 2015, 105
-
High-Throughput Sequencing Detects Minimal Residual Disease in Acute T Lymphoblastic Leukemia. 16 May 2012 Vol 4 Issue 134 134ra63
-
Immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene high-throughput sequencing quantifies minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and predicts post- transplantation relapse and survival. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1307-1313.
Next-generation sequencing and real-time quantitative PCR for minimal residual disease detection in B-cell disorders. Leukemia. 2014;28:1299-1307.
- High-throughput sequencing detects minimal residual disease in acute T lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:134ra163.
- Minimal residual disease quantification using consensus primers and high-throughput IGH sequencing predicts post-transplant relapse in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27:1659-1665.
- Minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Reviews Clin Oncol. 2013;10:460-471.
- The predictive strength of next-generation sequencing MRD detection for relapse compared with current methods in childhood ALL. BLOOD, 20 AUGUST 2015 x VOLUME 126, NUMBER 8
- Minimal residual disease diagnostics in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: need for sensitive, fast, and standardized technologies. Blood. 2015;125(26):3996-4009.
- Fast multiclonal clusterization of V(D)J recombinations from high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2014; 15:409.
- Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Current Status and Future Perspectives Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports, 2015, Page 1
