前言:
免疫组库(ImmuneRepertoire,IR)是指某个个体在任何特定时间点其循环系统中所有功能多样性B淋巴细胞和T淋巴细胞的总和。
TCR/BCR多样性超级丰富,理论上可达1015 – 1020种,所以我们的免疫系统机体才有可能识别不同种类的任何抗原。而当机体产生特异性免疫应答时,即T/B细胞对抗原产生特异性识别时,T/B细胞发生应激,TCR/BCR的多样性会发生变化,某种或某些T/B克隆会大量扩增,来对抗异己抗原。
TCR/BCR多样性主要是由V(D)J随机重组产生,而V、D、J基因本身又具有多样性,不同的T/B细胞克隆经基因重排、发生不同基因片段的连接,产生特定的(VDJ)基因和(VJ)基因,从而表达特异性TCR/BCR,这是TCR/BCR多样性产生的主要机制。
免疫组基因种类如此庞大,需要使用量化指标来评价TCR/BCR多样性,据此反映克隆有多少种不同类型,并且同时考虑到这些种类的个体分布之间的系统性关系,例如丰富性、差异性或均匀性等等。 此文整理了目前文献中经常采用的免疫组测序结果指数,与大家一起分享学习。
Clonality克隆性指数在于对TCR/BCR克隆扩增的衡量。Clonality值越大,表示有部分TCR/BCR克隆发生了很大频率的扩增。公式中,productive uniques 为样本中克隆种类总数,diversity为shannon多样性指数的值。
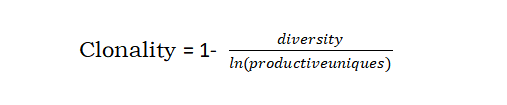
[1]Tumeh PC, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature.2014;515:568–571. doi: 10.1038/nature13954.
[2] Johnson D B, Frampton G M, Rioth M J, et al. Targeted next generation sequencing identifies markers of response to PD-1 blockade[J]. Cancer immunology research, 2016, 4(11): 959-967.
[3] Reuben A, Gittelman R, Gao J, et al. TCR repertoire intratumor heterogeneity in lo calized lung adenocarcinomas: an association with predicted neoantigen heterogeneity and postsurgical recurrence[J]. Cancer discovery, 2017, 7(10): 1088-1097.
Pielou’s用来评估克隆分布均匀程度,Pielou’s值越高,表示各克隆分布比较均匀, Pielou’s值越低,表示有一些特异性的克隆发生了扩增。公式中,pi为i总序列的比例,S为克隆类型总数。
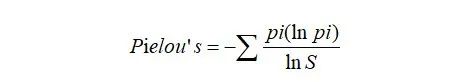
[1] A note on a generalization of Pielou’s equation.
[2] On a generalization of the global attractivity for a periodically forced Pielou’s equation.
[3] On the relationship between Pielou’s evenness and landscape domi v nance within the context of Hill’s diversity profiles.
香农指数用来衡量样本中TCR/BCR克隆的多样性,该指数能够描述两方面的信息①种类丰富度;②种类中个体分配上的均匀性(evenness)。香农指数越高,表示TCR/BCR的多样性越高。公式中,pi为第i个特异性克隆类型的频率。可以看出,香农既考虑了TCR/BCR克隆种类的多少,也考虑了每种克隆的均匀度(频率)。
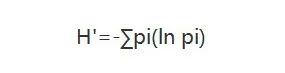
[1]Shannon, C. E. The mathematical theory of communication. 1963.MD Comput. 14, 306–317 (1997).
[2]Ruggiero E, Nicolay J P, Fronza R, et al. High-resolution analysis of the human T-cell receptor repertoire[J]. Nature communications, 2015, 6: 8081.
[3]Jia Q, Wu W, Wang Y, et al. Local mutational diversity drives intratumoral immune heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9.
我们通常不直接用Simpson index(D),它反映的是在同一个样本中随机的抽取2个个体,这两个个体来自同一个类的概率。故D值越大,多样性越低。这与直觉和逻辑不符。
为了解决这个问题,通常会用以下两种形式来表示:
(1)1减去D 即Gini-Simpson Diversity index
(2)1/D 即Inverse-Simpson index
Gini-Simpson代表意义是在同一个样本中随机抽取2个个体,这两个个体来自不同类的概率。这个值在0-1之间,指数越大,说明克隆的多样性越高。更加侧重反映克隆种类的均匀性。
(使用时有些地方也会将Gini-Simpson简化成Simpson,实际上这里是指Gini-Simpson,可根据公式区分)
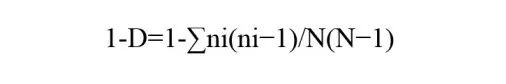
[1]Simpson, E. H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 163, 688 (1949).
[2]Jia Q, Wu W, Wang Y, et al. Local mutational diversity drives intratumoral immune heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9.
逆辛普森多样性指数是辛普森指数的倒数,逆辛普森指数越大,代表克隆的多样性越高。侧重反映高频克隆的多样性。
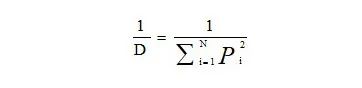
[1]Van Heijst J W J, Ceberio I, Lipuma L B, et al. Quantitative assessment of T cell repertoire recovery after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Nature medicine, 2013, 19(3): 372.
[2]Ruggiero E, Nicolay J P, Fronza R, et al. High-resolution analysis of the human T-cell receptor repertoire[J]. Nature communications, 2015, 6: 8081.
Hvj多样性指数,用来衡量样本中TCR克隆V-J基因组合使用的多样性。pi为第i个V-J基因片段组合使用类型的比例。反映的是对T细胞的扩增的衡量,也就是反映了T/B特异性识别抗原产生的应激后的复制增殖能力,值越大,表示克隆性扩增越多。
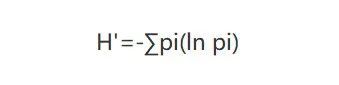
[1]Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Functionals of Discrete Distributions.2014.
[2]Information, Measurement, and Quantum Mechanics.1987.
DE50作为克隆性(克隆程度)的一个指标,衡量克隆性的均一程度,DE50值越高,代表各克隆分布比较均匀,DE50值越低,克隆性越高,代表有一些特异性的克隆发生了扩增。公式的计算方法为:克隆频率高于50%的所有克隆数目与克隆群中所有克隆数目的比值。

[1]Postow M A, Manuel M, Wong P, et al. Peripheral T cell receptor diversity is associated with clinical outcomes following ipilimumab treatment in metastatic melanoma[J]. Journal for immunotherapy of cancer, 2015, 3(1): 23.
[2]Hogan S A, Courtier A, Cheng P F, et al. Peripheral blood TCR repertoire profiling may facilitate patient stratification for immunotherapy against melanoma[J]. Cancer immunology research, 2019, 7(1): 77-85.
其他参数:
Entropy:计算某个特定的克隆出现在总的TCR repertoire中的概率,包含丰度和richness的信息。
什么是ImmuHub®技术?
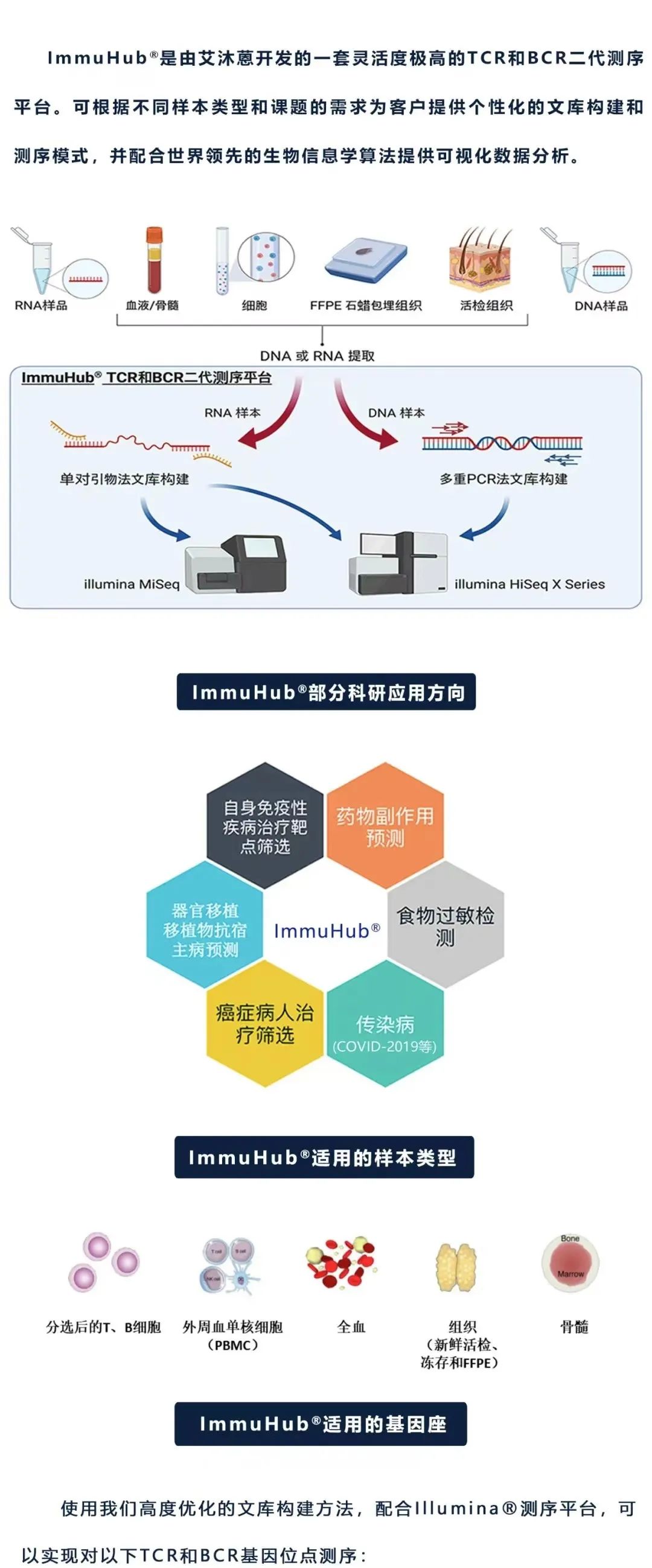
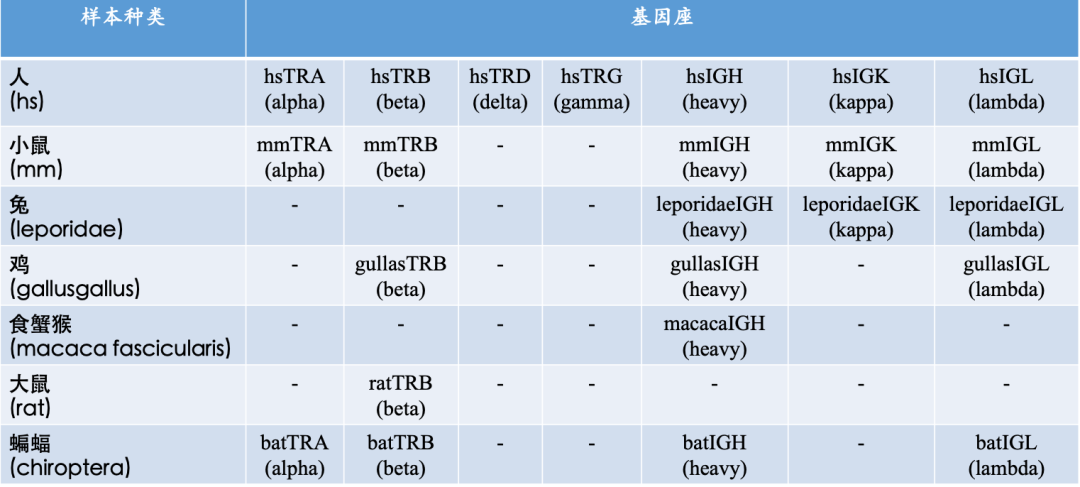
杭州艾沐蒽生物科技有限公司由美国芝加哥大学科研团队回国创办,是一家专注于通过解码适应性免疫系统来改变疾病的诊断和治疗,并致力于推进免疫驱动医学领域发展的国家高新技术企业。艾沐蒽站在适应性免疫系统研究的最前沿,自主研发的免疫医学平台可揭示和翻译适应性免疫系统的遗传密码,并能应用于癌症、自身免疫性疾病、传染性疾病等免疫介导性疾病的诊断、监测和治疗中。

