Seq-MRD®
什么是MRD?
Minimal Residual Disease
微小残留病 (Minimal Residual Disease, MRD) 是指白血病/淋巴瘤/骨髓瘤患者经治疗缓解后,体内仍残留少量癌细胞的状态,最终可能会引起疾病复发。因残留的癌细胞数量较少,不易察觉,因此需要更准确和灵敏地方法才能检测得到。
监测白血病、淋巴瘤和骨髓瘤患者在疾病整个治疗时期以及缓解后不同时间点的MRD水平对于患者疾病的治疗是非常重要的。近年来研究发现,微小残留病 (Minimal Residual Disease, MRD) 与上述癌症复发密切相关。MRD 是指癌症诱导缓解获 CR 后,体内仍有残留的癌变细胞,此为疾病复发的根源。对于病患而言,此时身体并没有任何复发症状和表现,传统的临床检测也很难发现。缓解诱导后的微小残留病水平具有重要的预后和治疗效果评估意义。缓解诱导之后,对于存在可检测微小残留病的患者,应进行连续微小残留病测定。为争取患者长期无病生存(Disease Free Survival time, DFS)和痊愈,必须对 MRD 进行动态监测,实施疗效评估,治疗指导及复发预测。
MRD如何检测?
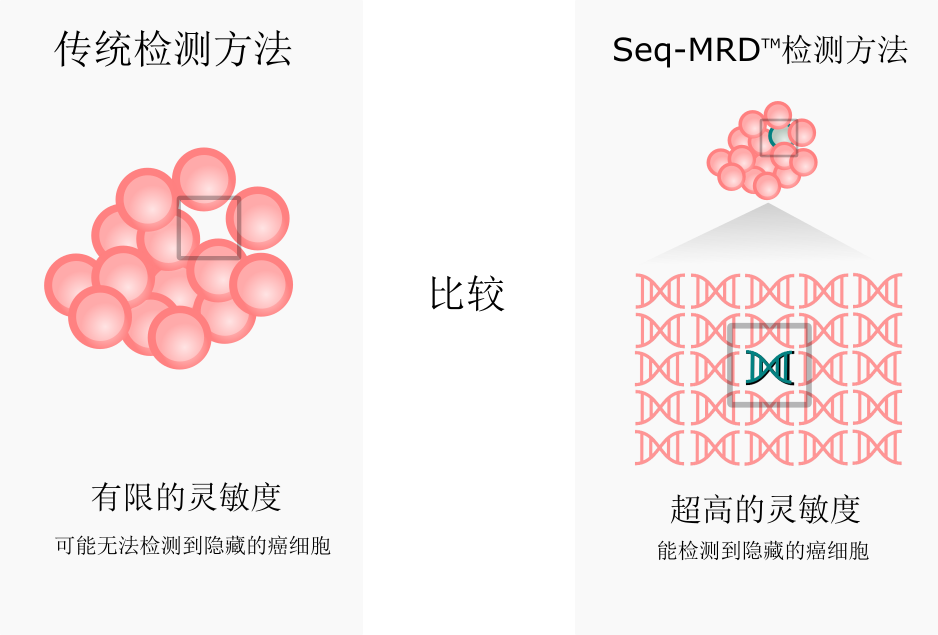
传统的MRD检测方法无法对疾病负荷进行准确定量,也不能高灵敏度地深度检测,这样暗藏的癌细胞有可能无法检测得到。而Seq-MRD®能准确定量检测出血液癌症患者特定癌细胞,为临床医生提供准确和高灵敏地MRD水平结果。

准确的MRD评估结果可指导临床医生对患者采取个性化治疗方法。采用相同的治疗方式,一些患者能获得完全缓解,而有些患者最终会复发。研究数据显示深度MRD缓解同患者病情改善有很大相关性。而缓解后MRD水平高的患者具有较高的复发危险,应进行较强的缓解后治疗,以改善长期疗效。医生在对病人连续治疗过程中可根据检测的MRD水平,预测评估患者对治疗的反应效果。检测患者MRD水平能在身体发生症状前,提早发现疾病进展情况,便于早期采取治疗,避免疾病复发。
MRD检测的未来
越来越多的研究者通过 MRD水平评估判断药物试验中药物的有效性,以及新型治疗方法的有效性。评估MRD水平同多种疾病治疗效果有预后判断意义,随着新型药物和治疗手段的出现,癌症缓解程度逐渐加深,更需要高灵敏度地对MRD检测。
Seq-MRD®检测技术具有如下特点:灵敏度高、应用广泛、符合监管要求、操作可重复、满足临床试验的高标准。所以该技术产品将会成为新的临床试验检测标准。
使用Seq-MRD®作为您MRD监控手段
二代测序方法作为新兴的MRD检测方法,也已受到国内外专家认可并推荐。2017年版国际临床实践指南(NCCN)、2016年版《中国成人急性淋巴细胞白血病诊断与治疗指南》和2017年版《中国多发性骨髓瘤诊治指南》均推荐高通量测序(NGS)作为MRD检测方法。
参考文献:
- Predictive value of next-generation sequencing-based minimal residual disease after CAR-T cell therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant 57, 1350–1353, 2022
-
Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology [NCCN Guidelines®] for Multiple Myeloma V.3.2017. ©National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2017. All rights reserved. Accessed May 11, 2017
-
Deep-sequencing approach for minimal residual disease detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2012;120:5173-5180.
-
Detection of Minimal Residual Disease Using Next Generation Sequencing for Antigen Receptor Gene Rearrangements in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia June 2015, 105
-
High-Throughput Sequencing Detects Minimal Residual Disease in Acute T Lymphoblastic Leukemia. 16 May 2012 Vol 4 Issue 134 134ra63
-
Immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene high-throughput sequencing quantifies minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and predicts post- transplantation relapse and survival. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1307-1313.
Next-generation sequencing and real-time quantitative PCR for minimal residual disease detection in B-cell disorders. Leukemia. 2014;28:1299-1307.
- High-throughput sequencing detects minimal residual disease in acute T lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:134ra163.
- Minimal residual disease quantification using consensus primers and high-throughput IGH sequencing predicts post-transplant relapse in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27:1659-1665.
- Minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Reviews Clin Oncol. 2013;10:460-471.
- The predictive strength of next-generation sequencing MRD detection for relapse compared with current methods in childhood ALL. BLOOD, 20 AUGUST 2015 x VOLUME 126, NUMBER 8
- Minimal residual disease diagnostics in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: need for sensitive, fast, and standardized technologies. Blood. 2015;125(26):3996-4009.
- Fast multiclonal clusterization of V(D)J recombinations from high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2014; 15:409.
- Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Current Status and Future Perspectives Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports, 2015, Page 1
